Oxalic Acid Treatment Table
Table updated Dec 20, 2023.
You can print this table directly from this page.
It is critical to mix and apply oxalic dribble correctly (5 mL between each frame of bees), or you risk seriously harming your bees! Be sure to read:
https://scientificbeekeeping.com/oxalic-acid-questions-answers-and-more-questions-part-1-of-2-parts/
https://scientificbeekeeping.com/the-learning-curve-part-3-the-natural-miticides/
https://scientificbeekeeping.com/oxalic-dribble-tips/
https://scientificbeekeeping.com/oxalic-acid-powerpoint-presentation/
Update Dec 20, 2023: We’ve experimented with using glycerin as the humectant instead of sugar. One possible advantage is that bees don’t like the taste of glycerin, and may thus be less likely to lick up the acid. The glycerin also helps the OA to adhere to the bees’ bodies for a longer period of time. I recently compared ratios of glycerin to water, and found that a 5% solution of glycerin to water results in good distribution of OA on the bees, and is less bothersome to the bees than a stronger concentration.
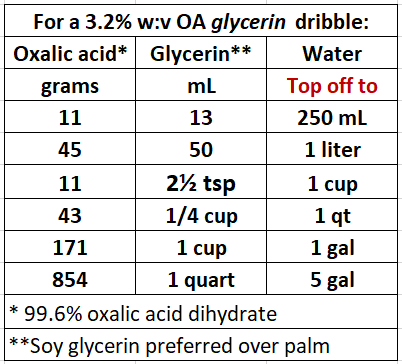
Please note that in the table below, the recipes are for weight: volume (w:v) formulas, for anhydrous oxalic acid, following the standard nomenclature used by European researchers. Anhydrous OA has a molecular weight of only 71.42% of that of the common oxalic acid dihydrate obtained by most beekeepers.
 *Distilled water may be necessary if you have “hard” (calcium-rich) water that reacts with the OA. To test, heat up some of your tap water in a clear glass container, then stir in a tsp of OA. If the water turns (and stays) cloudy white, there is too much calcium. Update April 2020: Oxalic acid will react with the calcium carbonate in hard water to form a precipitate of calcium oxalate, which you may see as a fine white layer on the bottom of the container. But this isn’t really something to worry about. The “hardest” water contains around 200 mg of calcium carbonate per liter. For an OA dribble, you use around 35 grams of OA per liter. The 200 mg of carbonate in that liter would neutralize only a tiny portion of the OA.
*Distilled water may be necessary if you have “hard” (calcium-rich) water that reacts with the OA. To test, heat up some of your tap water in a clear glass container, then stir in a tsp of OA. If the water turns (and stays) cloudy white, there is too much calcium. Update April 2020: Oxalic acid will react with the calcium carbonate in hard water to form a precipitate of calcium oxalate, which you may see as a fine white layer on the bottom of the container. But this isn’t really something to worry about. The “hardest” water contains around 200 mg of calcium carbonate per liter. For an OA dribble, you use around 35 grams of OA per liter. The 200 mg of carbonate in that liter would neutralize only a tiny portion of the OA.
**Granulated sugar can be roughly measured by volume –1 pint weighs ~1 lb; 1 qt weighs ~2 lbs.
Update 15 July 2019: A recent study by Toomema (https://doi.org/10.1080/00218839.2018.1486695), suggests that the oxalic dribble can be equally effective if a more dilute solution of OA in water alone (5 g OA dihydrate/1 L water) is applied at the greater rate of 20 mL/comb space of bees, rather than 5 mL. The above dose applies about half as much OA to the bees, but the greater amount of solution likely results in better dispersal. Toomema also recommends adding 1.2 g* of thymol per liter of heated solution, and then applying only 15 mL/comb space. Adding thymol caused irritation to the mites (and bees) and increases efficacy, but may cause additional adverse effects to the bees.
*Note that the solubility of thymol in water is only 0.9 g/L at 20°C, so some thymol would be expected to precipitate out as the syrup cooled. The point is that only a small amount of thymol will ever dissolve in sugar syrup.
Storage
Oxalic acid dissolved in water, especially if sugar or glycerin is added, degrades surprisingly rapidly. Use solutions soon, or store refrigerated. If a drop does not taste like strong lemon juice, it may have lost some of its acidity.
© Randy Oliver 2023



